Background¶
OOPS Observation Processing Flow¶
The flow of H(x) computation and QC filters application in OOPS is shown in the figure below.
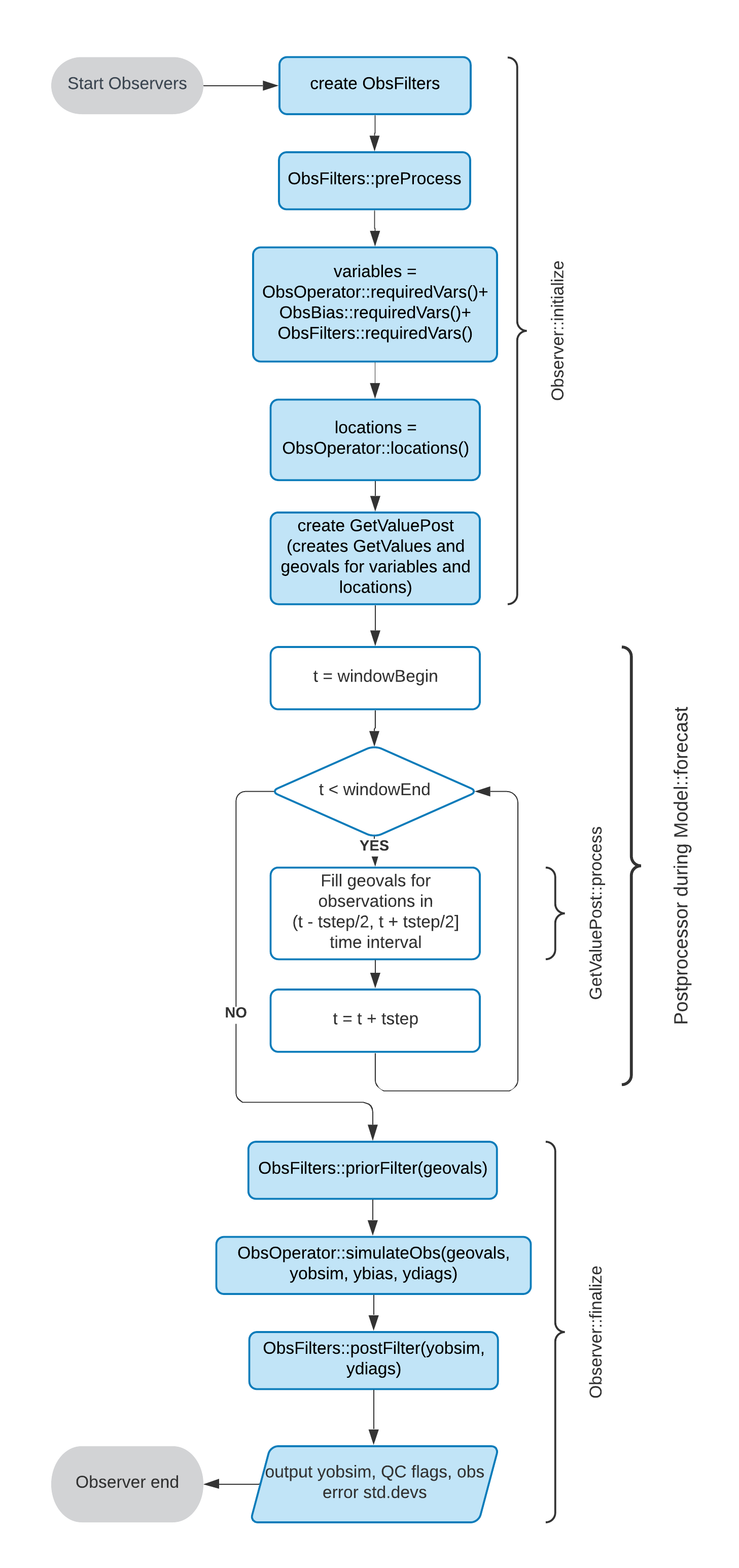
Fig. 14 Flow chart for computing H(x) and running QC filters¶
The Observer calls the preProcess method of ObsFilters before the loop over time steps. After the loop, it calls the priorFilter and postFilter methods just before and just after calling the simulateObs method of ObsOperator. The observation filters are very generic and can perform a number of tasks, but mostly they are used for quality control.
In variational data assimilation, the above flow happens inside of the observation term of the cost function (Jo) evaluation.
Observation Filters¶
- Observation filters have access to:
Observation values and metadata
Model values at observations locations (GeoVaLs)
Simulated observation value (for post-filter)
Their own private data
Most filters are written once and used with many observation types; several such generic filters already exist and are decribed below. Filters applied to observations from a specific ObsSpace need to be listed in the observations.obs filters section of the input YAML configuration file, together with any options controlling their behavior. Example:
observations:
- obs space:
name: AMSUA-NOAA19
obsdatain:
obsfile: Data/obs/testinput_tier_1/amsua_n19_obs_2018041500_m.nc4
simulated variables: [brightness_temperature]
channels: 1-15
obs filters:
- filter: Bounds Check
filter variables:
- name: brightness_temperature
channels: 1-15
minvalue: 100.0
maxvalue: 500.0
- filter: Background Check
filter variables:
- name: brightness_temperature
channels: 1-15
threshold: 3.0